| . |  |
. |
| . |  |
. |
|
by Staff Writers Portsmouth UK (SPX) Dec 07, 2018
Composite materials made from agricultural waste could be used to produce sustainable, lightweight and low-cost applications in the automotive and marine industries. A team of researchers, led by the University of Portsmouth, have developed a bio-composite material using date palm fibre biomass (biomass is a term that includes waste material from plants, food waste and sewage) that can be used in non-structural parts, such as car bumpers and door linings. The team also involved researchers from the University of Cambridge, INRA (Institut national de la recherche agronomique, a French public research institute dedicated to agricultural science) and University of Britanny, South. The date palm fibre polycaprolactone (PCL) bio-composite is completely biodegradable, renewable, sustainable and recyclable, unlike synthetic composites reinforced by glass and carbon fibres. In a study, published in the journal Industrial Crops and Products, the researchers tested the mechanical properties of the bio-composite. They found that the date palm fibre PCL had increased tensile strength and achieved better low-velocity impact resistance than traditional man-made composites. Dr Hom Dhakal, who leads the Advanced Materials and Manufacturing (AMM) Research Group at the University of Portsmouth and co-author of the study, said: "Investigating the suitability of date palm ?bres waste biomass as reinforcement in lightweight composite materials provides a tremendous opportunity of utilising this material to develop low-cost, sustainable and lightweight biocomposites. "The impact of this work would be extremely significant because these lightweight alternatives could help reduce the weight of vehicles, contributing to less fuel consumption and fewer C02 emissions. The sustainable materials can be produced using less energy than glass and carbon fibres and are biodegradable, therefore easier to recycle." The study is one of the first to provide a comprehensive assessment of the improved mechanical properties of date palm fibre PCL bio-composites. Date palm fibres are one of the most available natural fibres in North Africa and the Middle East. Date palm trees produce a large quantity of agriculture waste, which is burned or land-filled, causing serious environmental pollution as well as the destruction of important soil micro-organisms. The part of the date palm tree which is often used as ?bres is the sheath. The sheath is the part of the tree which surrounds the trunk of the plant. It is often torn lose when pruning the leaves. "It's a long journey," said Dr Dhakal, "and we have to have patience and perseverance to make an impact. The challenge is getting consistent, reliable properties. It takes a long time to convince people to use a new class of materials, such as natural fibre reinforced composites for non-structural and structural applications. "Meeting these challenges requires further research and innovation between academic institutions and industry." Dr Dhakal and his team have been working closely with industry to test the strength and viability of parts made from sustainable materials, such as date palm, flax, hemp and jute fibres. The AMM Research Group has been working in collaboration with researchers from institutions from around the world. In the last 18 months, the group has published many high impact factor papers in journals including the Composites Science and Technology, Composites Part A and Composites Part B. A recent collaborative study, published in the journal of Composite Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing explored the potential of waste leaf sheath date palm fibres for composite reinforcement.
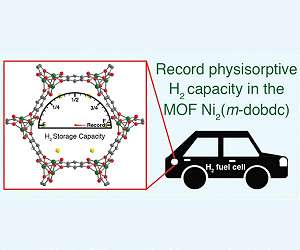
Paving the way for more efficient hydrogen cars Washington DC (SPX) Dec 06, 2018 Hydrogen-powered vehicles emit only water vapor from their tailpipes, offering a cleaner alternative to fossil-fuel-based transportation. But for hydrogen cars to become mainstream, scientists need to develop more efficient hydrogen-storage systems. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Chemistry of Materials have used metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) to set a new record for hydrogen storage capacity under normal operating conditions. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, in 2017 the U.S. ... read more
|
|||||||||||||
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2026 - SpaceDaily. All websites are published in Australia and are solely subject to Australian law and governed by Fair Use principals for news reporting and research purposes. By using our websites you consent to cookie based advertising. If you do not agree with this then you must stop using the websites from May 25, 2018. Privacy Statement. Additional information can be found here at About Us. |