| . |  |
. |
Baltimore MD (SPX) Aug 30, 2006 A new image taken with NASA's Hubble Space Telescope provides a detailed look at the tattered remains of a supernova explosion known as Cassiopeia A (Cas A). It is the youngest known remnant from a supernova explosion in the Milky Way. The new Hubble image shows the complex and intricate structure of the star's shattered fragments. The image is a composite made from 18 separate images taken in December 2004 using Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), and it shows the Cas A remnant as a broken ring of bright filamentary and clumpy stellar ejecta. These huge swirls of debris glow with the heat generated by the passage of a shockwave from the supernova blast. The various colors of the gaseous shards indicate differences in chemical composition. Bright green filaments are rich in oxygen, red and purple are sulfur, and blue are composed mostly of hydrogen and nitrogen. A supernova such as the one that resulted in Cas A is the explosive demise of a massive star that collapses under the weight of its own gravity. The collapsed star then blows its outer layers into space in an explosion that can briefly outshine its entire parent galaxy. Cas A is relatively young, estimated to be only about 340 years old. Hubble has observed it on several occasions to look for changes in the rapidly expanding filaments. In the latest observing campaign, two sets of images were taken, separated by nine months. Even in that short time, Hubble's razor-sharp images can observe the expansion of the remnant. Comparison of the two image sets shows that a faint stream of debris seen along the upper left side of the remnant is moving with high speed - up to 31 million miles per hour (fast enough to travel from Earth to the Moon in 30 seconds!). Cas A is located ten thousand light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Cassiopeia. Supernova explosions are the main source of elements more complex than oxygen, which are forged in the extreme conditions produced in these events. The analysis of such a nearby, relatively young and fresh example is extremely helpful in understanding the evolution of the universe. Related Links Hubble Herritage Project
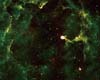 Paris, France (ESA) Aug 29, 2006
Paris, France (ESA) Aug 29, 2006AKARI, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) infrared astronomical satellite with ESA participation, is continuing its survey of the sky and its mapping of our cosmos in infrared light. New exciting images recently taken by AKARI depict scenes from the birth and death of stars. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2006 - SpaceDaily.AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA PortalReports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additionalcopyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |