| . |  |
. |
| . |  |
. |
|
by Staff Writers Beijing (XNA) Apr 19, 2022
Chinese scientists will soon have a new space-based tool to advance their research on the atmospheric environment and pollution. After in-orbit tests, the Atmospheric Environmental Surveyor satellite will start its monitoring operations and send data to scientists, according to its designers at the Shanghai Academy of Spaceflight Technology. The 2.6-metric ton satellite was launched by a Long March 4C carrier rocket on Saturday from the Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center in Shanxi province, and entered a sun-synchronous orbit 705 kilometers above Earth. It will be used to observe air pollution, greenhouse gases and other environmental elements. It will provide data for research on climate change and ecological changes, and will help to forecast agricultural yields and hazards, the designers said. The spacecraft carries five atmospheric monitoring devices, including an environmental monitoring instrument, a directional polarization camera and a particle observation scanning polarization meter, said researchers at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences who took part in the development of the scientific payload. It is the world's first satellite using a laser radar to detect carbon dioxide. It can also monitor other polluting gases such as nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide and formaldehyde. In addition, the craft can conduct quantitative observation of atmospheric particulate pollutants. Major users of data obtained by the satellite will be the Ministry of Ecology and Environment, the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs and the China Meteorological Administration. The satellite will give China a world-class capability to carry out atmospheric remote-sensing operations to help with the country's efforts in achieving low-carbon development and reducing pollution, said the China National Space Administration. The administration also said it will launch a satellite dedicated to measuring greenhouse gases in the near future. Several hours before the launch in Taiyuan, a Long March 3B carrier rocket blasted off from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center in Sichuan province on Friday and put the ChinaSat 6D communication satellite into orbit. That satellite, developed by the China Academy of Space Technology, is tasked with transmitting radio and television signals to islands in the South China Sea and small countries in the Pacific Ocean, its designers said. China has carried out 11 space launches so far this year. The nation's major space contractors announced at the start of 2022 that they planned to conduct more than 50 launches. Source: Xinhua News Agency
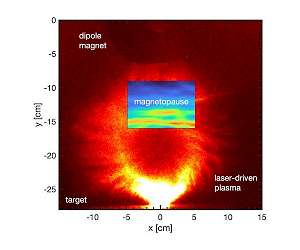
Modeling Earth's Magnetosphere in the Lab Washington DC (SPX) Apr 13, 2022 A magnetosphere forms around any magnetized object, such as a planet, that is immersed within a stream of ionized gas, called plasma. Because Earth possesses an intrinsic magnetic field, the planet is surrounded by a large magnetosphere that extends out into space, blocks lethal cosmic rays and particles from the sun and stars, and allows life itself to exist. In Physics of Plasmas, by AIP Publishing, scientists from Princeton, UCLA, and the Instituto Superior Tecnico, Portugal, report a method to ... read more
|
|||||||||||||
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2026 - SpaceDaily. All websites are published in Australia and are solely subject to Australian law and governed by Fair Use principals for news reporting and research purposes. By using our websites you consent to cookie based advertising. If you do not agree with this then you must stop using the websites from May 25, 2018. Privacy Statement. Additional information can be found here at About Us. |