| . |  |
. |
| . |  |
. |
|
by Staff Writers Washington DC (SPX) Nov 08, 2018
In the quest to replace fossil fuels, scientists are always on the lookout for alternative, environmentally friendly sources of energy. But who could have imagined a bionic mushroom that produces electricity? It sounds like something straight out of Alice in Wonderland, but researchers have now generated mushrooms patterned with energy-producing bacteria and an electrode network. They report their results in the ACS journal Nano Letters. Many examples of organisms that live closely together and interact with each other exist in nature. In some cases, this symbiotic relationship is mutually beneficial. A team of researchers led by Manu Mannoor and Sudeep Joshi from Stevens Institute of Technology wanted to engineer an artificial symbiosis between button mushrooms and cyanobacteria. In their scenario, the mushroom would provide shelter, moisture and nutrients, while bacteria 3D-printed on the mushroom's cap would supply energy by photosynthesis. Graphene nanoribbons printed alongside the bacteria could capture electrons released by the microbes during photosynthesis, producing bio-electricity. To make their bionic mushroom a reality, the researchers first 3D printed an electronic ink containing graphene nanoribbons onto the cap of a living mushroom in a branched pattern. They then printed a bio-ink containing cyanobacteria onto the cap in a spiral pattern, which intersected with the electronic ink at multiple points. At these sites, electrons could transfer through the outer membranes of the bacteria to the conductive network of graphene nanoribbons. Shining a light on the mushroom activated cyanobacterial photosynthesis, generating a current of about 65 nanoAmps. Although this current is insufficient to power an electronic device, the researchers say that an array of bionic mushrooms could generate enough current to light up an LED. The researchers are now working on ways to generate higher currents using this system. They say that this 3D-printing approach could be used to organize other bacterial species in complex arrangements to perform useful functions, such as bioluminescence.
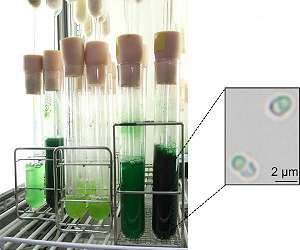
Scientists find a 'switch' to increase starch accumulation in algae Tokyo, Japan (SPX) Nov 05, 2018 Results from a collaborative study by Tokyo Institute of Technology and Tohoku University, Japan, raise prospects for large-scale production of algae-derived starch, a valuable bioresource for biofuels and other renewable materials. Such bio-based products have the potential to replace fossil fuels and contribute to the development of sustainable systems and societies. A "switch" controlling the level of starch content in algae has been discovered by a research team led by Sousuke Imamura at the L ... read more
|
|||||||||||||
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2026 - SpaceDaily. All websites are published in Australia and are solely subject to Australian law and governed by Fair Use principals for news reporting and research purposes. By using our websites you consent to cookie based advertising. If you do not agree with this then you must stop using the websites from May 25, 2018. Privacy Statement. Additional information can be found here at About Us. |