| . |  |
. |
The chances of the Earth being hit by a comet from beyond Pluto - a la Armageddon - are much lower than previously thought, according to new research by an ANU astronomer. Using computer simulations and data from an American military telescope, Dr Paul Francis, from the ANU Research School of Astronomy and Astrophysics at Mt Stromlo, has found there are seven times fewer comets in our solar system than previously thought. "I calculate that small comets, capable of destroying a city, only hit the Earth once every 40 million years or so," Dr Francis said. "Big continent-busting comets, as shown in the movies Armageddon and Deep Impact, are rarer still, only hitting once every 150 million years or so. So I don't loose sleep over it, but you're still more likely to be killed by a comet than to win the jackpot at Lotto." Previous estimates of the number of comets were based on the work of amateur astronomers, who for hundreds of years have been scanning the skies, looking for new comets. Previously, it was believed that these amateur astronomers were only spotting three per cent of the comets passing close to the Earth: the rest were thought to be missed because they were in the wrong part of the sky or were too faint. But Dr Francis found that the amateurs were doing better than anyone had realised - they were actually spotting 20 per cent of comets. There are therefore far fewer undiscovered comets. "The new data allowed us to count the number of faint and far-away comets that the amateurs had missed. And we found that they were pretty rare," Dr Francis said. These results apply to comets coming from beyond the orbit of Pluto, which is where most comets live. The Earth is still at risk of being hit by asteroids, and by so-called short-period comets - ones that come past repeatedly, like Halley's comet. "But asteroids and short-period comets come past again and again, so if we're clever enough we can find them all and predict which, if any, will hit the Earth," said Dr Francis. "If we find one on a collision course with the Earth, we would normally have hundreds of years warning in which to do something about it, like deflecting the asteroid. "The comets coming from beyond Pluto, so called long-period comets, are nastier, as they are totally unpredictable, and if we see one on a collision course we'd have at best one or two years warning - not long enough to do anything." Dr Francis' research has been accepted for publication in the Astrophysical Journal. It was based on computer simulations, published data from the Lincoln Near Earth Asteroid Research Project at White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico, and on data from amateur astronomers around the world. Related Links SpaceDaily Search SpaceDaily Subscribe To SpaceDaily Express 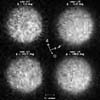 College Park MD (SPX) Sep 08, 2005
College Park MD (SPX) Sep 08, 2005Observations of 1 Ceres, the largest known asteroid, have revealed that the object may be a "mini planet," and may contain large amounts of pure water ice beneath its surface.
|
| ||||||||||
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2016 - Space Media Network. All websites are published in Australia and are solely subject to Australian law and governed by Fair Use principals for news reporting and research purposes. AFP, UPI and IANS news wire stories are copyright Agence France-Presse, United Press International and Indo-Asia News Service. ESA news reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement, agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by Space Media Network on any Web page published or hosted by Space Media Network. Privacy Statement All images and articles appearing on Space Media Network have been edited or digitally altered in some way. Any requests to remove copyright material will be acted upon in a timely and appropriate manner. Any attempt to extort money from Space Media Network will be ignored and reported to Australian Law Enforcement Agencies as a potential case of financial fraud involving the use of a telephonic carriage device or postal service. |