| . |  |
. |
Resembling the puffs of smoke and sparks from a summer fireworks display in this image from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, these delicate filaments are actually sheets of debris from a stellar explosion in a neighboring galaxy. Hubble's target was a supernova remnant within the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), a nearby, small companion galaxy to the Milky Way visible from the southern hemisphere. Denoted N 49, or DEM L 190, this remnant is from a massive star that died in a supernova blast whose light would have reached Earth thousands of years ago. This filamentary material will eventually be recycled into building new generations of stars in the LMC. Our own Sun and planets are constructed from similar debris of supernovae that exploded in the Milky Way billions of years ago. This seemingly gentle structure also harbors a very powerful spinning neutron star that may be the central remnant from the initial blast. It is quite common for the core of an exploded supernova star to become a spinning neutron star (also called a pulsar - because of the regular pulses of energy from the rotational spin) after the immediate shedding of the star's outer layers. In the case of N 49, not only is the neutron star spinning at a rate of once every 8 seconds, it also has a super-strong magnetic field a thousand trillion times stronger than Earth's magnetic field. This places this star into the exclusive class of objects called "magnetars." On March 5, 1979, this neutron star displayed a historic gamma-ray burst episode that was detected by numerous Earth-orbiting satellites. Gamma rays have a million or more times the energy of visible light photons. The Earth's atmosphere protects us by blocking gamma rays that originate from outer space. The neutron star in N 49 has had several subsequent gamma-ray emissions, and is now recognized as a "soft gamma-ray repeater." These objects are a peculiar class of stars producing gamma rays that are less energetic than those emitted by most gamma-ray bursters. The neutron star in N 49 is also emitting X-rays, whose energies are slightly less than that of soft gamma rays. High-resolution X-ray satellites have resolved a point source near the center of N 49, the likely X-ray counterpart of the soft gamma-ray repeater. Diffuse filaments and knots throughout the supernova remnant are also visible in X-ray. The filamentary features visible in the optical image represent the blast wave sweeping through the ambient interstellar medium and nearby dense molecular clouds. Today, N 49 is the target of investigations led by Hubble astronomers You-Hua Chu from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and Rosa Williams from the University of Massachusetts. Members of this science team are interested in understanding whether small cloudlets in the interstellar medium of the LMC may have a marked effect on the physical structure and evolution of this supernova remnant. The Hubble Heritage image of N 49 is a color representation of data taken in July 2000, with Hubble's Wide Field Planetary Camera 2. Color filters were used to sample light emitted by sulfur ([S II]), oxygen ([O III]), and hydrogen (H-alpha). The color image has been superimposed on a black-and-white image of stars in the same field also taken with Hubble. Image Credit: NASA and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) Acknowledgment: Y.-H. Chu (UIUC), S. Kulkarni (Caltech) and R. Rothschild (UCSD) Related Links The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) SpaceDaily Search SpaceDaily Subscribe To SpaceDaily Express 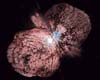 Geneva - Apr 22, 2003
Geneva - Apr 22, 2003A team of theoretical physicists, Shlomo Dado and Arnon Dar at the Technion, Israel Institute of Technology and Alvaro De Rujula CERN, the European Center for Nuclear Research, in Geneva, Switzerland, has developed a theory to account for the mysterious gamma ray bursts that come from the depths of the Universe.
|
| ||||||||||
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2016 - Space Media Network. All websites are published in Australia and are solely subject to Australian law and governed by Fair Use principals for news reporting and research purposes. AFP, UPI and IANS news wire stories are copyright Agence France-Presse, United Press International and Indo-Asia News Service. ESA news reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement, agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by Space Media Network on any Web page published or hosted by Space Media Network. Privacy Statement All images and articles appearing on Space Media Network have been edited or digitally altered in some way. Any requests to remove copyright material will be acted upon in a timely and appropriate manner. Any attempt to extort money from Space Media Network will be ignored and reported to Australian Law Enforcement Agencies as a potential case of financial fraud involving the use of a telephonic carriage device or postal service. |