| . |  |
. |
Sunlight, snow and sea salt are sometimes used to illustrate nature at its best. But new scientific evidence shows that, when combined, these forces provide a potent mixture for destroying ozone. Purdue University researchers, working with scientists from Battelle and the University of California, Irvine, discovered that bromine and chlorine, two chemicals found in sea salt, may initiate a series of chemical events that destroy ozone in the Arctic troposphere, the lowest part of the atmosphere. The findings, published in the Jan. 19 issue of the scientific journal Science, describe the role that bromine and chlorine play in a complex series of chemical reactions that occur each spring when, after several months of darkness, sunlight interacts with the snow in the Arctic region. The study traces the source of those chemical precursors to the salty minerals found in sea water that is carried into the snowpack in the form of tiny salt particles by wind and waves. "Bromine and chlorine have long been suspected as major players in this series of chemical events, but until now the source of these chemicals was unknown," says Paul Shepson, professor of atmospheric chemistry at Purdue. "Our findings indicate that this near-surface ozone depletion in the Arctic is a naturally occurring event." Ozone, a beneficial component of the earth's upper atmosphere, is a pollutant at the ground level but is essential to the health of the atmosphere, Shepson says. The findings may help scientists develop better models to simulate and predict long-term changes in the composition of the earth's atmosphere, he says. "Because three-quarters of the earth's surface is covered by ocean, we've uncovered a process we need to understand much better in terms of our ability to model ozone in the atmosphere." Current models don't take these interactions into account because scientists are only beginning to recognize and document the role snow and sea salt play in atmospheric chemistry. In 1986, scientists observed that, at polar sunrise, which occurs in March or April after several months of complete darkness, ozone in a thin layer of air over the Arctic Ocean is completely removed. "This was a big surprise to us, and it indicated that our understanding of atmospheric ozone, and the factors that lead to its production and depletion, is poor," Shepson says. Since then, scientists have found evidence that a number of chemicals that lay dormant in the snow can interact with sunlight to produce chemical "pollutants" -- such as nitric oxide, nitrogen dioxide, formaldehyde and bromine -- that impact the atmosphere's composition. Shepson and colleague Jan Bottenheim of Environment Canada led a research group to the Canadian Arctic last year to measure levels of bromine and chlorine in the snowpacks and analyze how sunlight interacts with these chemicals during the polar sunrise. >From a research site at the Canadian Forces base in Alert, Canada, the group measured levels of bromine and chlorine in the snow and air over a two-month period, beginning in early February. The bromine and chlorine measurements were conducted under the leadership of Chet Spicer of Battelle-Columbus, and Barbara Finlayson-Pitts of the University of California, Irvine. The measurements show that in mid-March, when the sun began to rise over the Arctic region, these elements increased in the air while decreasing in the snow. Because molecular bromine is short-lived in the atmosphere and can't be transported very far, Shepson and his colleagues began looking for sources of bromine from the local environment. "Sea salt is the only source of bromine in the Arctic," he says. Bromine and chlorine also play a role in destroying ozone in the upper atmosphere over the Arctic and Antarctic. In those cases the sources of bromine and chloride come primarily from human-derived pollutants, Shepson says. Though the study indicates that ozone-depletion is a naturally occurring process in the Arctic, the findings suggest that mixtures of snow and salt on roads in urban areas may also affect air quality, Shepson says. "The ingredients from what we observe in the Arctic are sometimes present in high concentrations on the streets of urban areas during the winter months," says Shepson, an expert in chlorine chemistry. "I wouldn't want to make predictions, but there could be a variety of chemical interactions that occur in urban, road-salted environments that we need to understand." Related Links Purdue University SpaceDaily Search SpaceDaily Subscribe To SpaceDaily Express 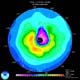 Boulder - October 5, 2000
Boulder - October 5, 2000Scientists from the Commerce Department's National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration report that measurements of this year's ozone hole at the South Pole show that ozone depletion occurred earlier there, but did not reach the very lowest values of some recent years.
|
| ||||||||||
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2016 - Space Media Network. All websites are published in Australia and are solely subject to Australian law and governed by Fair Use principals for news reporting and research purposes. AFP, UPI and IANS news wire stories are copyright Agence France-Presse, United Press International and Indo-Asia News Service. ESA news reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement, agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by Space Media Network on any Web page published or hosted by Space Media Network. Privacy Statement All images and articles appearing on Space Media Network have been edited or digitally altered in some way. Any requests to remove copyright material will be acted upon in a timely and appropriate manner. Any attempt to extort money from Space Media Network will be ignored and reported to Australian Law Enforcement Agencies as a potential case of financial fraud involving the use of a telephonic carriage device or postal service. |