| . |  |
. |
Using satellite and other data, scientists have discovered that sea surface temperatures and sea level pressure in the North Pacific have undergone unusual changes over the last five years. These changes to the North Pacific Ocean climate system are different from those that dominated for the past 50-80 years, which has led scientists to conclude that there is more than one key to the climate of that region than previously thought. According to a study by Nicholas Bond, J.E. Overland and P. Stabeno of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory, and M. Spillane of the University of Washington, during the last four winters from 1999-2002 (ranging from November to March) sea surface temperatures were cooler than normal along the U.S. west coast and warmer than normal in the coastal Gulf of Alaska. These conditions differ from those of the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO), thought to be the primary key that causes the climate of the North Pacific to change. As a result, the scientists believe that the conditions that have occurred since 1999 are independent of the PDO. The Pacific Decadal Oscillation is a basin-wide oceanic pattern similar to El Ni�o and La Ni�a but much larger. It lasts a couple of decades rather than a year or less like El Ni�o and La Ni�a. According to Bond, the unusual levels of pressure and temperature seen in the last five years are a departure from the pattern seen in the PDO, which represented the principal mode of long-term climate variability in the North Pacific for the 20th century. These results show that a single index such as the PDO is incomplete for characterizing the state of the North Pacific climate system. "Looking back over the past century, categorizing the climate signals as a pure PDO pattern would be simple-minded," said Bill Patzert, Oceanographer and Climatologist at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. "This research shows that although there are some characteristics of a PDO, there are some disturbances in the 'PDO force,' as the study showed using sea surface temperature and sea level pressure, Patzert noted. A good example is that some areas of North America are responding in a PDO-like response, and other places like Western Canada and Alaska are not experiencing cooler air temperatures expected from a simple PDO shift. Patzert praised his colleagues and noted that the lesson is that these climate patterns are constantly shifting, so Bond and Stabeno have reminded scientists that the decadal shifts in climate are not clean and simple. The change throughout the last five years in the North Pacific climate may also be having considerable impacts on the marine ecosystem. For example, during the recent period, ocean conditions were favorable to salmon and allowed them to return in greater numbers and reproduce more. In a classic PDO scenario, the salmon fisheries would collapse in Alaska and boom in Pacific Northwest, but they're booming in both places. "During the winters from 1999 through 2002 the North Pacific Ocean was subject to unusually or anomalously low sea level pressure in the Bering Sea and anomalously high sea level pressure north of Hawaii," Bond said. Sea level pressure is the weight of the air pressing down at sea level, and is on average 14.7 pounds per square inch. "At the same time, a broad band of unusually warm water extended eastward from the coast of China and a band of unusually cold water curved from off the coast of the lower 48 to north of Japan," he said. "The best sea surface temperature data we get are from satellites. We couldn't do this kind of research with ships and buoys, because they just don't have that kind of coverage," Bond said. "The bottom line is not to take your "satellite" eye off the climate system, because it's very changeable," Patzert said. Bond used NOAA's National Center for Environmental Prediction analysis of sea surface temperatures. Those temperatures are derived from the Polar Operational Environmental Satellite system, of which NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center is responsible for their construction, integration, and launch. "In the future, NOAA plans to include in their analysis, sea surface temperature data from NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite (TRMM), and the Aqua satellite's Advanced Microwave Radiometer and Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer instruments," said Richard Reynolds, research oceanographer with NOAA's National Climatic Data Center. Related Links NOAA SpaceDaily Search SpaceDaily Subscribe To SpaceDaily Express 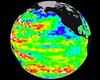 Pasadena - Mar 04, 2004
Pasadena - Mar 04, 2004Don't look for more sunny days while vacationing in paradise! A recent study of tropical oceans that used satellites including NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM), found that rain in the tropics will become more frequent as ocean temperatures rise.
|
| ||||||||||
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2016 - Space Media Network. All websites are published in Australia and are solely subject to Australian law and governed by Fair Use principals for news reporting and research purposes. AFP, UPI and IANS news wire stories are copyright Agence France-Presse, United Press International and Indo-Asia News Service. ESA news reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement, agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by Space Media Network on any Web page published or hosted by Space Media Network. Privacy Statement All images and articles appearing on Space Media Network have been edited or digitally altered in some way. Any requests to remove copyright material will be acted upon in a timely and appropriate manner. Any attempt to extort money from Space Media Network will be ignored and reported to Australian Law Enforcement Agencies as a potential case of financial fraud involving the use of a telephonic carriage device or postal service. |