| . |  |
. |
While observing a supernova in a distant galaxy with the FORS instrument on ESO's Very Large Telescope at the Paranal Observatory (Chile), astronomers were incredibly lucky to obtain serendipitously a high quality spectrum of a very large meteor in the terrestrial atmosphere. The VLT spectrograph provided a well calibrated spectrum, making it a reference in this field of research. From this spectrum, the temperature of the meteor trail was estimated to be about 4600 degrees centigrade. The serendipitous spectrum reveals the telltale meteor emissions of oxygen and nitrogen atoms and nitrogen molecules. The VLT spectrum was the first to reveal the far red range where carbon emission lines are predicted; the absence of the lines puts constraints on the role of atmospheric chemistry when life started on earth. Because the VLT is tuned to observe objects far out in space, it focuses at infinity. The meteor, being "only" 100 km above the telescope, therefore appears out of focus in the field of view.
Astronomers' luck At the time of this unlikely event, the telescope was performing a series of 20-minute spectroscopic exposures of a supernova in a distant galaxy in order to establish constraints on the dark energy content of the Universe. Thanks to its enormous light-collecting and magnifying power, the VLT recorded the spectrum of the meteor trail perpendicular to its path on one of these exposures. "We really hit the jackpot", says ESO astronomer Emmanuel Jehin: "Chances of capturing a meteor in the narrow slit of the FORS1 spectrograph are about as big as for me winning the national lottery." Meteor spectra have on occasion been obtained serendipitously during photographic star spectra surveys. But this is now maybe the only meteor spectrum recorded with a large telescope and a modern spectrograph. The spectrum covers the wavelength range from 637 to 1050 nm, which is dominated by emissions from air atoms and molecules in the meteor path and teach us about the collision processes in the wake of a meteoroid. The rapid motion of the meteor across the sky resulted in a very brief exposure while crossing the narrow spectrograph slit - only 1/50 of a millisecond - and despite the relative brightness of the meteor it was only thanks to the VLT's great light-gathering power that any record was procured. The meteor was estimated at magnitude -8, or nearly as bright as the first-quarter Moon. Although it is not possible to be sure from which shower this meteor belongs, a possible candidate is the Southern May Ophiuchid shower which appears from a direction just east of the bright star Antares. The shower contributes only one or two meteors per hour but was one of the stronger showers of that night.
Telltale emissions "We asked around to see if others in our country had witnessed the meteor, but it seems we at the VLT were the only ones, perhaps not too surprising as Paranal is located in the middle of the empty desert." And unfortunately for the astronomers, the MASCOT all-sky camera was not yet in operation at that time. The VLT spectrograph provided a well calibrated spectrum of the meteor emission, making it a reference in this field of research. The meteor emission results from collisions between air molecules, knocked to high speeds after initial collision with the meteoroid. Closer inspection of the spectrum revealed about 20 telltale meteor emissions of oxygen and nitrogen atoms and nitrogen molecules. The ratio of atomic and molecular emissions could be used as a "thermometer" to measure the conditions in the meteor-induced hot gas in the wake of the meteoroid, by means of laboratory measurements and meteor models that calibrate the VLT data.
From here to infinity "We later realised that this was due to the fact that, as seen by the VLT, the meteor trail was out of focus, even though it was 100 kilometres away!" The VLT is indeed focussed at infinity, which is perfect for most astronomical objects that it routinely observes. But not for meteoroids entering the atmosphere above Paranal. A point at 100 kilometres distance will appear as a small circle of diameter 15 arcsec at the VLT focal plane. This corresponds to roughly half of the maximum apparent diameter of Mars in the evening sky. It is the same effect as when you try to photograph your children with a forest in the background. If you focus your camera on the distant forest, then (in most cases) your children will be out of focus. Or to put this in another way, the VLT is clearly not very suited to observe ships passing by on the Pacific Ocean, just 12 km from Paranal.
No Trace of Carbon "We calculated that these lines should have been visible if all atmospheric carbon dioxide in the meteor path was dissociated into carbon and oxygen atoms," says Jenniskens, "but they were conspicuously absent". This observation is important because it sets new constraints on the efficiency of meteor-induced atmospheric chemistry at the time when life began on our planet.
Appendix: Cosmic showers Most meteoroids are completely destroyed at altitudes between 80 and 110 km, but some of the bigger ones make it to the ground. Here they may be collected as meteorites. Many meteoroids originate as fragments of asteroids and appear to be unaltered since the formation of the Solar System, some 4500 million years ago. Based on the peculiar composition of some meteorites, we know that a small fraction of meteoroids originate from the Moon, Mars or the large asteroid Vesta. They obviously result from major impacts on these bodies which blasted rock fragments into space. These fragments then orbit the Sun and may eventually collide with the Earth. Comets are another important source of meteoroids and perhaps the most spectacular. After many visits near the Sun, a comet "dirty-snowball" nucleus of ice and dust decays and fragments, leaving a trail of meteoroids along its orbit. Some "meteoroid streams" cross the earth's orbit and when our planet passes through them, some of these particles will enter the atmosphere. The outcome is a meteor shower - the most famous being the "Perseids" in the month of August and the "Leonids" in November. Thus, although meteors are referred to as "shooting" or "falling stars" in many languages, they are of a very different nature. Related Links ESO SpaceDaily Search SpaceDaily Subscribe To SpaceDaily Express 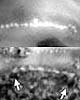 Moffett Field CA (SPX) Jul 22, 2004
Moffett Field CA (SPX) Jul 22, 2004The scientific debate over whether a meteorite contains evidence of past life on Mars continues to intensify, with colleagues of the team that announced the possibility in 1996 revealing new findings that may cast doubt on some of that earlier work.
|
| ||||||||||
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2016 - Space Media Network. All websites are published in Australia and are solely subject to Australian law and governed by Fair Use principals for news reporting and research purposes. AFP, UPI and IANS news wire stories are copyright Agence France-Presse, United Press International and Indo-Asia News Service. ESA news reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement, agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by Space Media Network on any Web page published or hosted by Space Media Network. Privacy Statement All images and articles appearing on Space Media Network have been edited or digitally altered in some way. Any requests to remove copyright material will be acted upon in a timely and appropriate manner. Any attempt to extort money from Space Media Network will be ignored and reported to Australian Law Enforcement Agencies as a potential case of financial fraud involving the use of a telephonic carriage device or postal service. |