| . |  |
. |
Claims of evidence of living bacterial cells entering the Earth's upper atmosphere from space has come from a joint project involving Indian and UK scientists. The first positive identification of extraterrestrial microbial life will be reported on Sunday, 29 July 2001 at the Astrobiology session of the 46th Annual SPIE meeting in San Diego, USA by Professor Chandra Wickramasinghe of Cardiff University. He will speak on behalf of an international team led by Professor Jayant Narlikar, Director of the Inter-Universities Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics in Pune, India. Samples of stratospheric air were collected on 21 January 2001 under the most stringent aseptic conditions by Indian scientists using the Indian Space Research Organisation's (ISRO) cryogenic sampler payload flown on balloons from the Tata Institute Balloon Launching facility in Hyderabad. Part of the samples sent to Cardiff were analysed by a team at Cardiff University led by Professor David Lloyd and assisted by Melanie Harris. Commenting on the results, Professor Wickramasinghe said: "There is now unambiguous evidence for the presence of clumps of living cells in air samples from as high as 41 kilometres, well above the local tropopause (16 km), above which no air from lower down would normally be transported." The detection was made using a fluorescent cyanine dye which is only taken up by the membranes of living cells. The variation with height of the distribution of such cells indicates strongly that the clumps of bacterial cells are falling from space. The daily input of such biological material is provisionally estimated as about one third of a tonne over the entire planet. This new evidence provides strong support for the Panspermia theory of Sir Fred Hoyle and Chandra Wickramasinghe. "We have argued for more than two decades that terrestrial life was brought down to Earth by comets and that cometary material containing microorganisms must still be reaching us in large quantities," said Professor Wickramasinghe. Related Links Cardiff University SpaceDaily Search SpaceDaily Subscribe To SpaceDaily Express 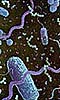 Moffett Field - July 23, 2001
Moffett Field - July 23, 2001As advanced microscopes enable us to peer deeper into the realms of inner space, biologists have been faced with a vexing question: Is there a size limit on life? If so, then just how small can something be before it can no longer be defined as "life"?
|
| ||||||||||
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2016 - Space Media Network. All websites are published in Australia and are solely subject to Australian law and governed by Fair Use principals for news reporting and research purposes. AFP, UPI and IANS news wire stories are copyright Agence France-Presse, United Press International and Indo-Asia News Service. ESA news reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement, agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by Space Media Network on any Web page published or hosted by Space Media Network. Privacy Statement All images and articles appearing on Space Media Network have been edited or digitally altered in some way. Any requests to remove copyright material will be acted upon in a timely and appropriate manner. Any attempt to extort money from Space Media Network will be ignored and reported to Australian Law Enforcement Agencies as a potential case of financial fraud involving the use of a telephonic carriage device or postal service. |