| . |  |
. |
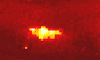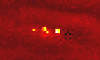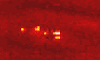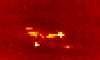 Pasadena - February 9, 2000 - Using data from the Galileo spacecraft currently in orbit around Jupiter, scientists have discovered that thunderstorms beneath the upper cloud cover are supplying energy to the planet's colorful large-scale weather patterns-including the 300-year-old Great Red Spot.
Pasadena - February 9, 2000 - Using data from the Galileo spacecraft currently in orbit around Jupiter, scientists have discovered that thunderstorms beneath the upper cloud cover are supplying energy to the planet's colorful large-scale weather patterns-including the 300-year-old Great Red Spot.In two articles in the February 10 issue of the British journal Nature and an article in the current issue of the journal Icarus, Caltech planetary science professor Andrew Ingersoll and his colleagues from Cornell, NASA, and UCLA write that lightning storms on the giant planet are clearly associated with the eddies that supply energy to the large-scale weather patterns. Their conclusion is possible because Galileo can provide daytime photos of the cloud structure when lightning is not visible, and nighttime photos of the same area a couple of hours later clearly showing the lightning. "You don't usually see the thunderstorms or the lightning strikes because the ammonia clouds in the upper atmosphere obscure them," says Ingersoll. "But when Galileo passes over the night side, you can see bright flashes that let you infer the depth and the intensity of the lightning bolts." Especially fortuitous are the Jovian nights when there is a bit of moonshine from one of the large moons such as Io, says Ingersoll. When there is no moonshine, the Galileo images show small blobs of glow from the lightning flashes, but nothing else. But when the upper cloud covers are illuminated at night by moonshine, the pictures show both the glow from the lightning some 100 kilometers below as well as eddies being roiled by the turbulence of the thunderclouds. The association of the eddies with lightning is especially noteworthy in the new papers, Ingersoll says. Planetary scientists have known for some years that Jupiter had lightning; and in fact they have known since the Voyager flyby that the zonal jets and long-lived storms are kept alive by soaking up the energy of smaller eddies. But they did not know until now that the eddies themselves were fed by thunderstorms below. "The lightning indicates that there's water down there, because nothing else can condense at a depth of 80 or 100 kilometers," he says. "So we can use lightning as a beacon that points to the place where there are rapidly falling raindrops and rapidly rising air columns-a source of energy for the eddies. "The eddies, in turn, get pulled apart by shear flow and give up their energy to these large-scale features. So ultimately, the Great Red Spot gets its energy and stays alive by eating these eddies." Adding credence to the interpretation is the fact that the anticyclonic rotation (clockwise in the northern hemisphere and counterclockwise in the southern) of the eddies is consistent with the outflow from a convective thunderstorm. Their poleward drift is consistent with anticyclones being sucked into Jupiter's powerful westward jets. Ingersoll is lead author of the Nature paper that interprets the new Galileo data. The other authors are Peter Gierasch and Don Banfield of Cornell University; and Ashwin Vasavada of UCLA. (Banfield and Vasavada are Ingersoll's former doctoral students at Caltech). Gierasch is lead author of the other Nature paper, which announces the discovery of moist convection on Jupiter. The other authors are Ingersoll; Banfield; Vasavada; Shawn Ewald of Caltech; Paul Helfenstein and Amy Simon-Miller, both of Cornell; and Herb Breneman and David Senske, both of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). The authors of the Icarus paper are Ingersoll; Vasavada; Senske; Breneman; William Borucki of NASA Ames Research Center; Blane Little and Clifford Anger, both of ITRES Research in Calgary, Alberta; and the Galileo SSI Team.
JOVIAN DREAMS
|
| |||||||||
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2016 - Space Media Network. All websites are published in Australia and are solely subject to Australian law and governed by Fair Use principals for news reporting and research purposes. AFP, UPI and IANS news wire stories are copyright Agence France-Presse, United Press International and Indo-Asia News Service. ESA news reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement, agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by Space Media Network on any Web page published or hosted by Space Media Network. Privacy Statement All images and articles appearing on Space Media Network have been edited or digitally altered in some way. Any requests to remove copyright material will be acted upon in a timely and appropriate manner. Any attempt to extort money from Space Media Network will be ignored and reported to Australian Law Enforcement Agencies as a potential case of financial fraud involving the use of a telephonic carriage device or postal service. |