| . |  |
. |
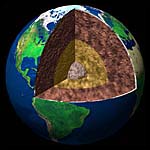 Baltimore - November 23, 1999 - One of the world's biggest cold fronts might be under our feet rather than over our heads, according to results from earth scientists at The Johns Hopkins University.
Baltimore - November 23, 1999 - One of the world's biggest cold fronts might be under our feet rather than over our heads, according to results from earth scientists at The Johns Hopkins University.Writing in this week's issue of Science, Hopkins researchers describe a laboratory experiment designed to model conditions in the outer core of the Earth, which is composed of molten iron. The laboratory results point to the possibility that a thin jet of relatively cold molten iron is streaming down across the liquid outer core from an area in the mid-Pacific to Earth's solid iron inner core. Seismic data of the Earth has led to a model of the interior that partitions it into a core, mantle, and crust. The crust is approximately 30 kilometers thick. The mantle is approximately 2,840 kilometers thick, and the core radius is approximately 3,500 kilometers thick. Each partition can be further divided into smaller regions. The crust can be classified as oceanic or continental, the mantle as upper and lower, and the core as outer liquid and inner solid. Pictured in this cutaway view of the Earth is the crust, mantle, liquid outer core, and solid inner core. This image is Copyright � 1998 by Calvin J. Hamilton Ikuro Sumita, a postdoctoral researcher at Hopkins and lead author on the paper, cautions that the new model is a "working hypothesis" there are many questions and concerns still to be addressed. But he has developed several tantalizingly direct ways to use the model to answer questions about observations relating to the Earth's core. The Earth's molten outer core lies beneath the rocky mantle, which includes the surface. Earth scientists think of the mantle as the "master" that directs the activity of the outer core, which acts like a "slave" in response. Because of this close relationship, understanding the core's activity should help scientists better understand the mantle's behavior. It's not possible, however, to directly observe the outer core. Scientists can image the solid inner core using energy from earthquakes, known as seismic waves. But this reveals little of the liquid outer core. "What we have to rely on instead to study the outer core is Earth's magnetic field, which is produced by the flow of molten iron," says Sumita. Scientists can link changes in the strength and direction of magnetic fields above ground to the ebb and flow of molten iron below ground, Sumita explains. "For example, we can interpret the westward motion of the magnetic field patches as a manifestation of the westward flow in the core," he notes.
A heater was placed at one spot on the rim of the hemisphere to imitate the uneven transfer of heat between the mantle and the outer core. Because the direction of the centrifugal force in the experiment is opposite to that of the Earth's gravity, this corresponds to a cold region found in the lower mantle of the Earth which causes a downward flow in the core. Researchers set the model rotating, injected a fluorescent dye into the water, and filmed the resulting patterns. A thin spiral-shaped jet moving opposite the direction of the rest of the water soon emerged. In a manner similar to a weather front, the jet, which spiraled down to the solid sphere at the model's center, marked out the boundary between hot, high pressure areas and cool, low pressure zones in the water. "We know that the seismic waves travel unusually fast in the lowermost region of the mantle beneath East Asia," says Sumita. "This is often interpreted as being due to a cold plate which has sunk into the bottom of the mantle from the surface of the Earth. Such a cold region would cause the core to lose a great deal of heat there." A spiraling jet of cold iron starting east of that area could account for irregularities in the magnetic patterns observed over the Pacific. For example, there are fewer westward drifting magnetic patches in this area, which could be a result of the front blocking the westward flow of iron as well as the upward flow of hot iron. "It may be that the colder mass of fluid west of the front causes the iron to solidify more in one region and accounts for this uneven east-west buildup," Sumita explains. Missing in Sumita's theory is a mechanism that would keep the cold spot in East Asia cold for a long time. The buildup in the Earth's inner core is very slow, and to have shaped that buildup the spiral would need to have been in place for millions of years. Another potential wrinkle is the possibility that solid inner core rotates, in which case the buildup should be more even. "To follow up," Sumita says, "I will have to summarize the conditions needed for the existence of this jet and the front based upon the experiments I did with different heater magnitudes and sizes." Further evidence on the potential merits of Sumita and Olson's model could come from high-resolution seismic imaging of the structure of the lowermost mantle and the inner core. Olson published a study in Nature last week that examined the flow near the polar region of the outer core. That study is complementary to the present work, which examines the flow in the lower latitudes of the outer core. Sumita's research was supported by the Research Fellowships of the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science for Young Scientists. The experiments were supported by the Geophysics Program of the National Science Foundation.
TERRADAILY.COM
|
| |||||||||
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2016 - Space Media Network. All websites are published in Australia and are solely subject to Australian law and governed by Fair Use principals for news reporting and research purposes. AFP, UPI and IANS news wire stories are copyright Agence France-Presse, United Press International and Indo-Asia News Service. ESA news reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement, agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by Space Media Network on any Web page published or hosted by Space Media Network. Privacy Statement All images and articles appearing on Space Media Network have been edited or digitally altered in some way. Any requests to remove copyright material will be acted upon in a timely and appropriate manner. Any attempt to extort money from Space Media Network will be ignored and reported to Australian Law Enforcement Agencies as a potential case of financial fraud involving the use of a telephonic carriage device or postal service. |