| . |  |
. |
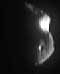 Deep Space - July 29, 1999 - NASA's Deep Space 1 experimental spacecraft successfully flew closely above the surface of asteroid 9969 Braille at 9:46 p.m. Pacific time Wednesday, July 28 (04:46 Universal Time July 29), using a sophisticated new space autopilot system, exceeding 100 percent of the mission's objectives.
Deep Space - July 29, 1999 - NASA's Deep Space 1 experimental spacecraft successfully flew closely above the surface of asteroid 9969 Braille at 9:46 p.m. Pacific time Wednesday, July 28 (04:46 Universal Time July 29), using a sophisticated new space autopilot system, exceeding 100 percent of the mission's objectives.An exultant operations team looked on as preliminary data returned to the Deep Space 1 operations control area at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, CA, indicating that the AutoNav autopilot system skillfully flew the spacecraft to a face-to-face closeup with asteroid Braille. "This is a dramatic finale to an amazingly successful mission," said Dr. Marc Rayman, chief mission engineer and deputy mission manager. "With AutoNav's successful piloting of the spacecraft, we've completed the testing and validation of the 12 new technologies onboard and possibly acquired important science data, including photos." Data from the spacecraft will be analyzed in coming days to determine the actual flyby distance, which at about 15 kilometers (less than 10 miles), was by far the closest flyby of an asteroid ever attempted. Ten minutes after the flyby, when the spacecraft signals reached Earth after a 10-minute journey, the team burst into spontaneous applause at the news that the spacecraft was turning back to face the asteroid. The turn was indicated by a marked Doppler shift, a clear early indicator of a successful encounter. Like a siren whose pitch changes after passing by, the Doppler shift indicates movement past an object. Launched Oct. 24, 1998, Deep Space 1 is the first mission under NASA's New Millennium Program, which tests new technologies for future space and Earth-observing missions. The technologies that have been tested on Deep Space 1 will help make future science spacecraft smaller, less expensive, more autonomous and capable of more independent decision-making so that they rely less on tracking and intervention by ground controllers. Of the 12 new technologies on board, all but the spacecraft's autonomous navigation system had been completely tested since launch. With the asteroid encounter, AutoNav finished its last five percent of testing. Making the flyby all the more memorable -- and serving as a testimonial to the team's quick ability to think on its feet -- was the fact that the spacecraft experienced a "safing" event earlier in the day, starting at about 5 a.m. PDT on July 28 and ending at about 11 a.m. PDT. A small software glitch, now fully diagnosed, was detected by Deep Space 1's fault-detection software, which triggered a protective program that causes several events: the spacecraft halts non-critical activity, orients its solar panels toward the Sun, points light and heat-sensitive instruments away from the Sun and reverts to its low-gain antenna while awaiting new commands. "This has been by far the most challenging, dramatic and stressful day on the project," said Rayman. "The last 16 hours before the flyby were really, really exciting. We had the safing event, we recovered from it and we managed to squeeze in a trajectory correction maneuver to update Deep Space 1's flight path." Science results will be downlinked in a series of telemetry sessions over the next several days. During the flyby, a spectrometer and imaging instrument took black-and-white photographs and images taken in infrared light, while a second instrument observed the three-dimensional distribution of ions and electrons, or plasma, in the area. A science update covering science results is scheduled to take place at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif., on Tuesday, August 3, at 10 a.m. PDT. It will be broadcast live on NASA TV.
Deep Space 1 Reports From Spacer.Com
|
| |||||||||||
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2016 - Space Media Network. All websites are published in Australia and are solely subject to Australian law and governed by Fair Use principals for news reporting and research purposes. AFP, UPI and IANS news wire stories are copyright Agence France-Presse, United Press International and Indo-Asia News Service. ESA news reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement, agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by Space Media Network on any Web page published or hosted by Space Media Network. Privacy Statement All images and articles appearing on Space Media Network have been edited or digitally altered in some way. Any requests to remove copyright material will be acted upon in a timely and appropriate manner. Any attempt to extort money from Space Media Network will be ignored and reported to Australian Law Enforcement Agencies as a potential case of financial fraud involving the use of a telephonic carriage device or postal service. |