| . |  |
. |
ESA's comet chaser mission Rosetta took these infrared and visible images of Earth and the Moon, during the Earth fly-by of 4/5 March 2005 while on its way to Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko. These images, now processed, are part of the first scientific data obtained by Rosetta. "The Earth fly-by represented the first real chance to calibrate and validate the performance of the Rosetta's instruments on a real space object, to make sure everything works fine at the final target," said Angioletta Coradini, Principal Investigator for the Visible and Infrared Thermal Imaging Spectrometer (VIRTIS) instrument. "Although we were just calibrating VIRTIS during the Earth fly-by last month, we obtained images of Earth and the Moon which have a high scientific content," she added. VIRTIS is a very powerful instrument capable of examining the physical condition and composition of space objects. On 4 and 5 March, before closest approach to Earth and from a distance of 400 000 kilometres from our Moon, Rosetta's VIRTIS took these images with high resolution in visible and infrared light. In these images, only a small portion of the Moon surface was illuminated (between 19% and 32%).
In the first, VIRTIS is catching the thermal radiation coming uniformly from the lunar surface. In the second VIRTIS is focusing on the solar radiation reflected by the surface. In the next image (right) it is possible to distinguish Oceanus Procellarum, Kepler Crater and Mare Humorum. The corresponding spectral analysis (chemical 'finger-printing') gives indications of the mineralogical differences between highlands and 'seas' or 'maria'. For instance, it was possible to see marked differences in the abundance of two kinds of rocks known as pyroxene and olivine. On 5 March, after the closest approach to Earth, VIRTIS then took a series of high-resolution images of our planet in visible and infrared light from a distance of 250 000 kilometres. Only 49% of the Earth surface was visible from Rosetta. In this animation (right) of visible images, red, green and blue colours are used to show a true-colour Earth. The infrared images in the next animation are taken in the so-called 'thermal' infrared, which shows the heat emitted from Earth's surface. This animation shows the complex dynamics of Earth's atmosphere. Once at Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko in 2014, VIRTIS will be used to determine the composition and the nature of the solid nucleus and the gases present in the comet's coma. In combination with the other Rosetta instruments, it will also help the selection of the 'touchdown' site for the Rosetta lander Philae. Before then, Rosetta will make more cosmic loops to reach the comet, and its instruments will collect new data about planets, asteroids and comets. The next encounter with Earth is planned for November 2007. VIRTIS as been developed by a large consortium of European scientists, with major contribution by Italy, France and Germany. Related Links Arianespace Astrium Space DLR SpaceDaily Search SpaceDaily Subscribe To SpaceDaily Express 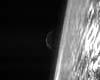 Paris (ESA) Mar 10, 2005
Paris (ESA) Mar 10, 2005During last Friday's Earth-skimming fly-by, Rosetta's Navigation Cameras captured images looking down and ahead. While cloud formations, coastlines and continents are clearly visible, the best photo shows the Moon rising above the Pacific, taken as the craft headed away from our home planet and out into space.
|
| |||||||||||
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2016 - Space Media Network. All websites are published in Australia and are solely subject to Australian law and governed by Fair Use principals for news reporting and research purposes. AFP, UPI and IANS news wire stories are copyright Agence France-Presse, United Press International and Indo-Asia News Service. ESA news reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement, agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by Space Media Network on any Web page published or hosted by Space Media Network. Privacy Statement All images and articles appearing on Space Media Network have been edited or digitally altered in some way. Any requests to remove copyright material will be acted upon in a timely and appropriate manner. Any attempt to extort money from Space Media Network will be ignored and reported to Australian Law Enforcement Agencies as a potential case of financial fraud involving the use of a telephonic carriage device or postal service. |